Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
Selected image –
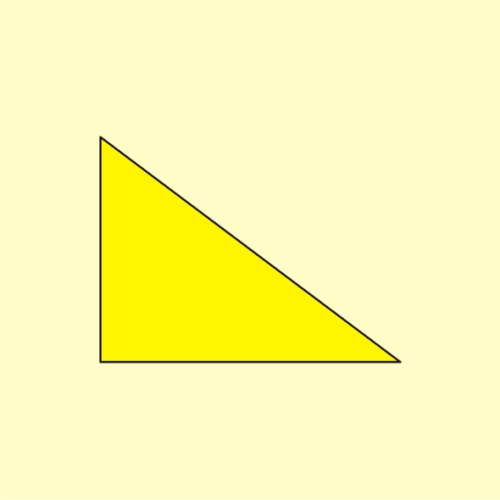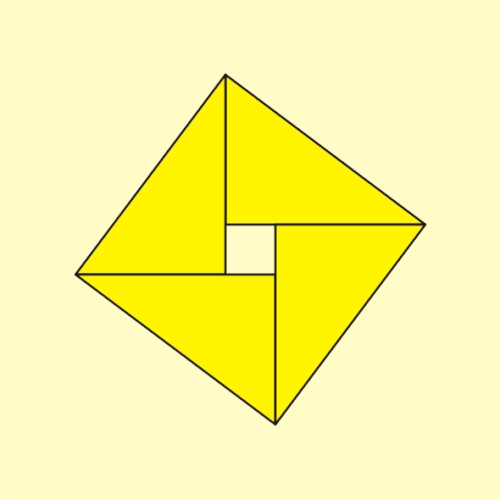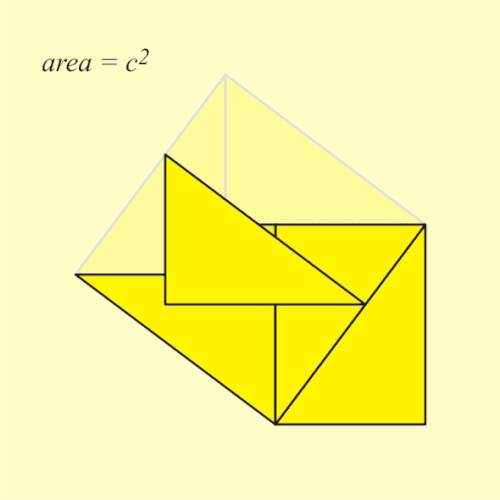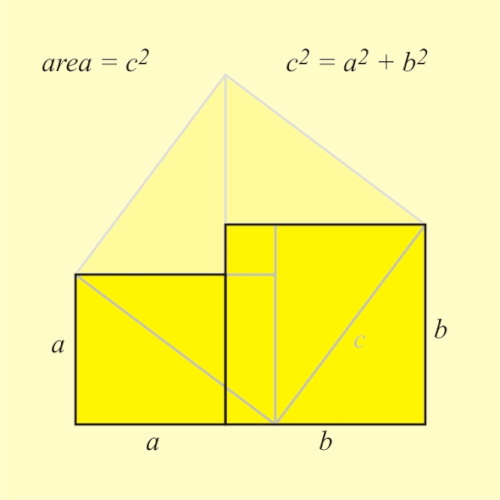
Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that The Math Myth advocates for American high schools to stop requiring advanced algebra?
- ... that people in Madagascar perform algebra on tree seeds in order to tell the future?
- ... that Fairleigh Dickinson's upset victory over Purdue was the biggest upset in terms of point spread in NCAA tournament history, with Purdue being a 23+1⁄2-point favorite?
- ... that multiple mathematics competitions have made use of Sophie Germain's identity?
- ... that despite published scholarship to the contrary, Andrew Planta neither received a doctorate nor taught mathematics at Erlangen?
- ... that the word algebra is derived from an Arabic term for the surgical treatment of bonesetting?
- ... that in the aftermath of the American Civil War, the only Black-led organization providing teachers to formerly enslaved people was the African Civilization Society?
- ... that a folded paper lantern shows that certain mathematical definitions of surface area are incorrect?
More did you know –

- ...that it is unknown whether π and e are algebraically independent?
- ...that a nonconvex polygon with three convex vertices is called a pseudotriangle?
- ...that it is possible for a three-dimensional figure to have a finite volume but infinite surface area, such as Gabriel's Horn?
- ... that as the dimension of a hypersphere tends to infinity, its "volume" (content) tends to 0?
- ...that the primality of a number can be determined using only a single division using Wilson's Theorem?
- ...that the line separating the numerator and denominator of a fraction is called a solidus if written as a diagonal line or a vinculum if written as a horizontal line?
- ...that a monkey hitting keys at random on a typewriter keyboard for an infinite amount of time will almost surely type the complete works of William Shakespeare?
Selected article –
 |
| Mathematics department in Göttingen where Hilbert worked from 1895 until his retirement in 1930 Image credit: Daniel Schwen |
David Hilbert (January 23, 1862, Wehlau, Prussia–February 14, 1943, Göttingen, Germany) was a German mathematician, recognized as one of the most influential mathematicians of the 19th and early 20th centuries. He established his reputation as a great mathematician and scientist by inventing or developing a broad range of ideas, such as invariant theory, the axiomization of geometry, and the notion of Hilbert space, one of the foundations of functional analysis. Hilbert and his students supplied significant portions of the mathematic infrastructure required for quantum mechanics and general relativity. He is one of the founders of proof theory, mathematical logic, and the distinction between mathematics and metamathematics, and warmly defended Cantor's set theory and transfinite numbers. A famous example of his world leadership in mathematics is his 1900 presentation of a set of problems that set the course for much of the mathematical research of the 20th century. (Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
| General | Foundations | Number theory | Discrete mathematics |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Algebra | Analysis | Geometry and topology | Applied mathematics |
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus